



| Advanced Java Services | FlowLayout |




|
A flow layout arranges components in a left-to-right flow, much like lines of text in a paragraph. Flow layouts are typically used to arrange buttons in a panel. It will arrange buttons left to right until no more buttons fit on the same line. Each line is centered.
| Konstanten | |
| Typ | Name der Konstante |
| static int | CENTER This value indicates that each row of components should be centered. |
| static int | LEADING This value indicates that each row of components should be justified to the leading edge of the container's orientation, for example, to the left in left-to-right orientations. |
| static int | LEFT This value indicates that each row of components should be left-justified. |
| static int | RIGHT This value indicates that each row of components should be right-justified. |
| static int | TRAILING This value indicates that each row of components should be justified to the trailing edge of the container's orientation, for example, to the right in left-to-right orientations. |
| Konstruktoren | |
| FlowLayout() | Constructs a new FlowLayout with a centered alignment and a default 5-unit horizontal and vertical gap. |
| FlowLayout(int align) | Constructs a new FlowLayout with the specified alignment and a default 5-unit horizontal and vertical gap. |
| FlowLayout(int align, int hgap, int vgap) | Creates a new flow layout manager with the indicated alignment and the indicated horizontal and vertical gaps. |
| Methoden | |
| Returntyp | Name der Methode |
| int | getAlignment() Gets the alignment for this layout. |
| void | setAlignment(int align) Sets the alignment for this layout. |
| int | getHgap() Returns the horizontal gap between components. |
| void | setHgap(int hgap) Sets the horizontal gap between components. |
| int | getVgap() Returns the vertical gap between components. |
| void | setVgap(int vgap) Sets the vertical gap between components. |
Im Vergleich zu BorderLayout ist die Arbeitsweise von FlowLayout ziemlich simpel. Flowlayout ordnet die Komponenten von links nach rechts und von oben nach unten in der Reihenfolge an, in der sie in den Container aufgenommen worden sind. Ein "Zeilenumbruch" findet dann statt, wenn eine Komponente nicht mehr Platz hat in einer Zeile. Dies hat zur Folge, daß sich das Layout bei Vergrößerung oder Verkleinerung des Containers völlig ändert, was meist alles andere als schön ist. Allerdings geht FlowLayout mit der Größe der aufgenommenen Komponenten behutsam um. Es berücksichtigt immer die Angaben, die die Methode getPreferedSize() liefert. Zusammengefaßt:
FlowLayout fl = new FlowLayout(); //fl.setHgap(30); //fl.setVgap(20); //fl.setAlignment(FlowLayout.RIGHT); container.setLayout(fl);
oder
FlowLayout fl = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT, 30, 20); container.setLayout(fl);
container.add(komponente1); container.add(komponente2); // etc.
Hier noch ein komplettes Beispiel mit Screenshot
/* ==================================================--------- *\
FlowLayoutDemo.java
\* ==================================================--------- */
import java.awt.* ;
import javax.swing.*;
public class FlowLayoutDemo extends JFrame
{
private JComponent conPane;
private JButton button1 = new JButton("Knopf 1");
private JButton button2 = new JButton("Knopf 2");
private JButton button3 = new JButton("Knopf 3");
public FlowLayoutDemo()
{
conPane = (JComponent)this.getContentPane();
conPane.setToolTipText("ContentPane");
FlowLayout fl = new FlowLayout();
fl.setHgap(30);
fl.setVgap(20);
//fl.setAlignment(FlowLayout.RIGHT);
conPane.setLayout(fl);
button1.setBackground( Color.cyan );
button1.setPreferredSize( new Dimension(80,60) ) ;
conPane.add(button1);
button2.setBackground( Color.yellow );
button2.setPreferredSize( new Dimension(120,40) ) ;
conPane.add(button2, BorderLayout.NORTH);
button3.setBackground( Color.green );
button3.setPreferredSize( new Dimension(100,80) ) ;
conPane.add(button3, BorderLayout.EAST);
initFrame() ;
}
private void initFrame()
{
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE) ;
setLocation(150,150) ;
setSize(500,250);
setTitle(" FlowLayoutDemo Alignment is LEFT");
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
FlowLayoutDemo wnd = new FlowLayoutDemo();
}
}
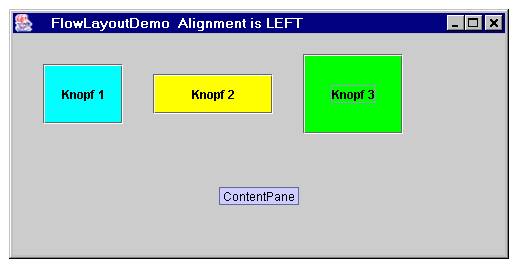
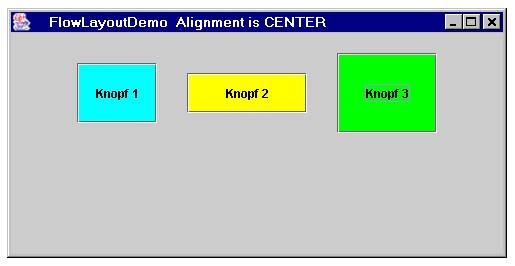
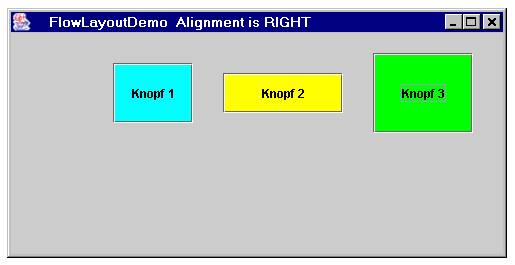
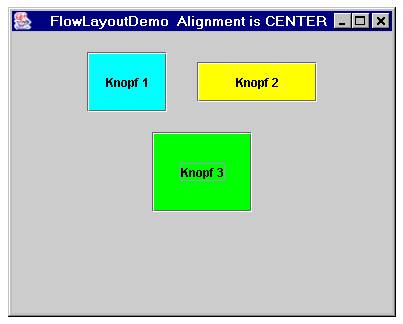
Verkleinert man das Fenster, so macht FlowLayout einen Zeilenumbruch
|
|




|